- Exploit DB: An archive of exploits and vulnerable software by Offensive Security. The site collects exploits from submissions and mailing lists and concentrates them in a single database.
- Hacked Gadgets: A resource for DIY project documentation as well as general gadget and technology news.
- Hakin9: E-magazine offering in-depth looks at both attack and defense techniques and concentrates on difficult technical issues.
- Metasploit: Find security issues, verify vulnerability mitigations & manage security assessments with Metasploit. Get the worlds best penetration testing software now.
- HackRead: HackRead is a News Platform that centers on InfoSec, Cyber Crime, Privacy, Surveillance, and Hacking News with full-scale reviews on Social Media Platforms.
- KitPloit: Leading source of Security Tools, Hacking Tools, CyberSecurity and Network Security.
- The Hacker News: The Hacker News — most trusted and widely-acknowledged online cyber security news magazine with in-depth technical coverage for cybersecurity.
- Packet Storm: Information Security Services, News, Files, Tools, Exploits, Advisories and Whitepapers.
- Phrack Magazine: Digital hacking magazine.
Tuesday, June 30, 2020
9 Useful Websites for Hackers 2018
Monday, June 29, 2020
re: please send me the Facebook traffic offer
ancient-ufo-pictures.htmlnoreply
here it is, social website traffic:
http://www.mgdots.co/detail.php?id=113
Full details attached
Regards
Vertie Scalzo �
Unsubscribe option is available on the footer of our website
Tuesday, June 16, 2020
Greetings from Mrs. Suzette E.
Dear safwanmohamad85.blogminda,
My name is Mrs. Suzette Engelhorn, a German citizen. I am a widow suffering from breast cancer and renal failure, as a result I may not last till the next two months according to my doctor's report. I was married to my late husband Mr. Ruprecht Engelhorn who worked with BASF (Badische Anilin und Soda Fabrik) Germany, and we were married for many years without a child before his death.
I am 52 years old woman.I inherited the sum of sum of €3.2 million Euro from my late husband, and I am in serious need of a good and honest person who will claim the funds from the Bank where it was deposited and funds use for donations to less-privileged and orphanage homes, building schools for the destitute and disaster affected people.
I decided to contact you for this donation as part of my contribution to help mankind and i would be happy anywhere i may be.I do not need any telephone communication in this regards because of my present health condition in accordance to my doctor's guideline report, get back to me through my direct email at engelhornmrssuzette@gmail.
Best regards.
Mrs. Suzette Engelhorn
Monday, June 15, 2020
PRODUCT INQUIRY
Dear safwanmohamad85.blogminda,
We are interested in your Products which you displayed in the site and we want to purchase some of the products.
Please send us more information about your company for our ref. with your conditions and terms as below,
*Delivery time
*Payment term ( LC or TT )
*Minimum order quantity
Best Regards
Peter Kim
(Export Manager)
KH-TECH CO., LTD
A.74, Hyeomnyeok-ro, Siheung-si, Gyeonggi-do,
Republic of Korea.
Tel.+82-31-497-2050~5
Fax.+82-31-497-2056
Email: exportkhoto@yahoo.com
re: Rank 1st in google with Content Marketing Strategy
Get your business to the next level with a solid Content Marketing strategy
http://www.str8-creative.io/product/content-marketing/
Regards
Refugio Allshouse
Unsubscribe option is available on the footer of our website
Thursday, June 11, 2020
Insecurities Of WhatsApp's, Signal's, And Threema's Group Chats
In this blog post, we aim to focus on the practical impact and the found weaknesses identified by our analysis. The interested reader may also look into our paper for more details.
Our Aim and What We Were Looking For
End-to-end encryption protects the confidentiality of communication that is forwarded via central servers to the designated receivers. As a consequence, neither parties on the network route of the messages, nor the provider of the central server (e.g. the WhatsApp server) should be able to read any information out of the observation of the communication. In particular, no other user of the application should have access to the communication. Further it might be desirable to require that also the messages' integrity is end-to-end protected and that a sender is informed about the delivery state of sent messages. |
| Delivery state information in Signal (upper screenshot) and WhatsApp (lower screenshot) |
In a two party scenario, this analysis is rather fixed to two components of the protocol: the key establishment between both parties and the communication channel protection using the established key (mostly consisting of an encryption algorithm and a scheme for providing integrity like MACs or signature schemes).
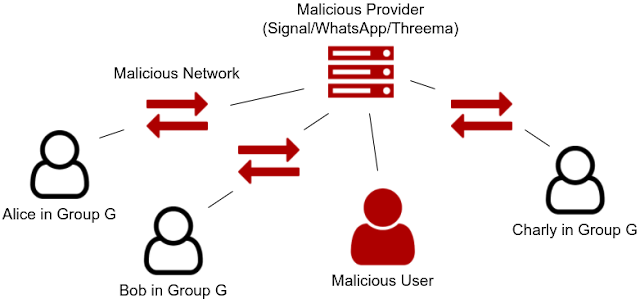 |
| Regarded attackers |
In a group setting, the same attackers apply (network, provider, other users). However the requirements for secure communication differ. It is further necessary that only group members can write to and read content from the group. Additionally, only administrators of the group are able to add new members.
In addition to these standard requirements, we also evaluated the protocols' security guarantees if the client's secrets were revealed (forward secrecy and future secrecy).
Our Approach
We analyzed the mentioned protocols by reading the source code and debugging the apps. We also used alternative open source implementations of Threema and WhatsApp as a help and we traced the network traffic. When using alternative implementations, we only took incoming traffic into account, which was generated by official applications. Thereby we extracted the protocol descriptions and evaluated them regarding the defined requirements.Our Findings
In WhatsApp and Threema, the provider was able to manipulate the set of members. Threema only allowed the provider to rewind the set of members to a previous state. As a consequence previously removed members could have been added to the group again. The WhatsApp provider is able to arbitrarily manipulate the member set. Thereby further members and administrators can be added to the group. Since the authenticity of group manipulation is not protected, the WhatsApp provider can set the real group administrator as the source of manipulation even though this administrator was not active.Since Signal's key exchange protocol provides future secrecy, we also evaluated the protocol's ability to recover into a secure group state after a member's state was compromised. The essential weakness here is that a sender only needs to know the static group ID to send a message to the group. If a group member receives a message with the correct group ID, no verification regarding the current member set takes place but the message is directly added to the group communication. Consequently it is sufficient to retrieve the group ID in order to send messages to the group. Since Signal treats content messages the same way as messages for the manipulation of the group set, an attacker who knows the group ID can add herself to the group and thereby read the subsequent group communication.
In addition to this, in all cases the delivery state of sent messages was not securely provided. Threema's group chats do not inform the sender about the delivery state while Signal and WhatsApp do not protect the delivery information on the end-to-end layer. Therefore the central provider can forge this information and drop messages without letting the communicating parties detect this.
Also the order of messages was manipulable for the providers of the applications such that the provider is able to deliver the messages in a different order than they were sent. Threema's weakness of rewinding a group state results from missing replay attack protection.
Impact of Weaknesses
Even though end-to-end encryption is implemented in all analyzed applications, the central providers can largely manipulate the communication in groups and partially also read it.In all applications, the provider can undetectably drop and reorder messages during the delivery and thereby manipulate the view of the communication such that further attacks can be obfuscated.
The central servers of WhatsApp can be used to add arbitrary users to groups and thereby receive their communication.
To achieve the same result for Signal, it suffices to retrieve the group ID. An earlier member who left the group once still knows this ID since it is static. However, in contrast to WhatsApp, the origin of the manipulation is correctly displayed in the Signal application (which was not the fact when we started our analysis).
As a result, the end-to-end protection of WhatsApp is not sufficient to reach confidentiality in groups. For Signal no future secrecy is reached in groups and Threema was vulnerable to replay attacks which resulted in further weaknesses.
Responsible Disclosure
We disclosed our findings to the developers and received varying response. Threema updated their protocol in version 3.14 such that our attacks are not feasible anymore. Moxie Marlinspike responded that Signal is "working on an entirely new group mechanism that we should be deploying soon". WhatsApp did not hold out the prospect of fixing the described vulnerabilities (Update 01/18: According to Facebook's Security Head, the invite links make a fix more difficult [1]; we proposed a way to solve this issue [2]).[1] https://twitter.com/alexstamos/status/951169036947107840
[2] https://web-in-security.blogspot.de/2018/01/group-instant-messaging-why-baming.html
Related links
Open Sesame (Dlink - CVE-2012-4046)
The basic functionality of the application is as follows:
- Application sends out a UDP broadcast on port 5978
- Camera sees the broadcast on port 5978 and inspects the payload – if it sees that the initial part of the payload contains "FF FF FF FF FF FF" it responds (UDP broadcast port 5978) with an encoded payload with its own MAC address
- Application retrieves the camera's response and creates another UDP broadcast but this time it sets the payload to contain the target camera's MAC address, this encoded value contains the command to send over the password
- Camera sees the broadcast on port 5978 and checks that it is meant for it by inspecting the MAC address that has been specified in the payload, it responds with an encoded payload that contains its password (base64 encoded)
After spending some time with the application in a debugger I found what looked like it was responsible for the decoding of the encoded values that are passed:
 |
| super exciting screen shot. |
| Command | Comments | |
| .JGE SHORT 0A729D36 | ; stage1 | |
| ./MOV EDX,DWORD PTR SS:[LOCAL.2] | ; set EDX to our 1st stage half decoded buffer | |
| .|MOV ECX,DWORD PTR SS:[LOCAL.4] | ; set ECX to our current count/offset | |
| .|MOV EAX,DWORD PTR SS:[LOCAL.3] | ; set EAX to our base64 encoded payload | |
| .|MOVSX EAX,BYTE PTR DS:[EAX] | ; set EAX to the current value in our base64 payload | |
| .|MOV AL,BYTE PTR DS:[EAX+0A841934] | ; set EAX/AL to a hardcoded offset of its value table is at 0a841934 | |
| .|MOV BYTE PTR DS:[ECX+EDX],AL | ; ECX = Offset, EDX = start of our half-decoded buffer, write our current byte there | |
| .|INC DWORD PTR SS:[LOCAL.4] | ; increment our offset/count | |
| .|INC DWORD PTR SS:[LOCAL.3] | ; increment our base64 buffer to next value | |
| .|MOV EDX,DWORD PTR SS:[LOCAL.4] | ; set EDX to our counter | |
| .|CMP EDX,DWORD PTR SS:[ARG.2] | ; compare EDX (counter) to our total size | |
| .\JL SHORT 0A729D13 | ; jump back if we have not finished half decoding our input value | |
| .MOV ECX,DWORD PTR SS:[ARG.3] | ; Looks like this will point at our decoded buffer | |
| .MOV DWORD PTR SS:[LOCAL.5],ECX | ; set Arg5 to our decoded destination | |
| .MOV EAX,DWORD PTR SS:[LOCAL.2] | ; set EAX to our half-decoded buffer | |
| .MOV DWORD PTR SS:[LOCAL.3],EAX | ; set arg3 to point at our half-decoded buffer | |
| .MOV EDX,DWORD PTR SS:[ARG.4] | ; ???? 1500 decimal | |
| .XOR ECX,ECX | ; clear ECX | |
| .MOV DWORD PTR DS:[EDX],ECX | ; clear out arg4 value | |
| .XOR EAX,EAX | ; clear out EAX | |
| .MOV DWORD PTR SS:[LOCAL.6],EAX | ; clear out local.6 | |
| .JMP SHORT 0A729DAE | ; JUMP | |
| ./MOV EDX,DWORD PTR SS:[LOCAL.3] | ; move our current half-decoded dword position into EDX | |
| .|MOV CL,BYTE PTR DS:[EDX] | ; move our current byte into ECX (CL) (dword[0]) | |
| .|SHL ECX,2 | ; shift left 2 dword[0] | |
| .|MOV EAX,DWORD PTR SS:[LOCAL.3] | ; move our current dword position into EAX | |
| .|MOVSX EDX,BYTE PTR DS:[EAX+1] | ; move our current dword position + 1 (dword[1]) into EDX | |
| .|SAR EDX,4 | ; shift right 4 dword[1] | |
| .|ADD CL,DL | ; add (shift left 2 dword[0]) + (shift right 4 dword[1]) | |
| .|MOV EAX,DWORD PTR SS:[LOCAL.5] | ; set EAX to our current decoded buffer position | |
| .|MOV BYTE PTR DS:[EAX],CL | ; write our decoded (dword[0]) value to or decoded buffer | |
| .|INC DWORD PTR SS:[LOCAL.5] | ; increment our position in the decoded buffer | |
| .|MOV EDX,DWORD PTR SS:[LOCAL.3] | ; set EDX to our current dword position | |
| .|MOV CL,BYTE PTR DS:[EDX+1] | ; set ECX to dword[1] | |
| .|SHL ECX,4 | ; left shift 4 dword[1] | |
| .|MOV EAX,DWORD PTR SS:[LOCAL.3] | ; set EAX to our current dword position | |
| .|MOVSX EDX,BYTE PTR DS:[EAX+2] | ; set EDX to dword[2] | |
| .|SAR EDX,2 | ; shift right 2 dword[2] | |
| .|ADD CL,DL | ; add (left shift 4 dword[1]) + (right shift 2 dword[2]) | |
| .|MOV EAX,DWORD PTR SS:[LOCAL.5] | ; set EAX to our next spot in the decoded buffer | |
| .|MOV BYTE PTR DS:[EAX],CL | ; write our decoded value into our decoded buffer | |
| .|INC DWORD PTR SS:[LOCAL.5] | ; move to the next spot in our decoded buffer | |
| .|MOV EDX,DWORD PTR SS:[LOCAL.3] | ; set EDX to our current half-decoded dword | |
| .|MOV CL,BYTE PTR DS:[EDX+2] | ; set ECX dword[2] | |
| .|SHL ECX,6 | ; shift left 6 dword[2] | |
| .|MOV EAX,DWORD PTR SS:[LOCAL.3] | ; set EAX to our current half-decoded dword | |
| .|ADD CL,BYTE PTR DS:[EAX+3] | ; add dword[2] + dword[3] | |
| .|MOV EDX,DWORD PTR SS:[LOCAL.5] | ; set EDX to point at our next spot in our decoded buffer | |
| .|MOV BYTE PTR DS:[EDX],CL | ; write our decoded byte to our decoded buffer | |
| .|INC DWORD PTR SS:[LOCAL.5] | ; move to the next spot in our decoded buffer | |
| .|ADD DWORD PTR SS:[LOCAL.3],4 | ; increment our encoded buffer to point at our next dword | |
| .|MOV ECX,DWORD PTR SS:[ARG.4] | ; set ECX to our current offset? | |
| .|ADD DWORD PTR DS:[ECX],3 | ; add 3 to our current offset? | |
| .|ADD DWORD PTR SS:[LOCAL.6],4 | ; add 4 to our byte counter?? | |
| .|MOV EAX,DWORD PTR SS:[ARG.2] | ; move total size into EAX | |
| .|ADD EAX,-4 | ; subtract 4 from total size | |
| .|CMP EAX,DWORD PTR SS:[LOCAL.6] | ; compare our total bytes to read bytes | |
| .\JG SHORT 0A729D50 | ; jump back if we are not done | |
| .MOV EDX,DWORD PTR SS:[LOCAL.3] | ; set EDX to our last DWORD of encoded buffer | |
| .MOVSX ECX,BYTE PTR DS:[EDX+3] | ; set ECX to dword[3] last byte of our half-decoded dword (dword + 3) | |
| .INC ECX | ; increment the value of dword[3] | |
| .JE SHORT 0A729E1E | ||
| .MOV EAX,DWORD PTR SS:[LOCAL.3] | ; set EAX to our current half-decoded dword | |
| .MOV DL,BYTE PTR DS:[EAX] | ; set EDX (DL) to dword[0] | |
| .SHL EDX,2 | ; shift left 2 dword[0] | |
| .MOV ECX,DWORD PTR SS:[LOCAL.3] | ; set ECX to our current encoded dword position | |
| .MOVSX EAX,BYTE PTR DS:[ECX+1] | ; set EAX to dword[1] | |
| .SAR EAX,4 | ; shift right 4 dword[1] | |
| .ADD DL,AL | ; add (shifted left 2 dword[0]) + (shifted right 4 dword[1]) | |
| .MOV ECX,DWORD PTR SS:[LOCAL.5] | ; set ECX to point at our next spot in our decoded buffer | |
| .MOV BYTE PTR DS:[ECX],DL | ; write our decoded value (EDX/DL) to our decoded buffer | |
| .INC DWORD PTR SS:[LOCAL.5] | ; move to the next spot in our decoded buffer | |
| .MOV EDX,DWORD PTR SS:[LOCAL.3] | ; set EDX to point at our dword | |
| .MOV AL,BYTE PTR DS:[EDX+1] | ; set EAX/AL to dword[1] | |
| .SHL EAX,4 | ; shift left 4 dword[1] | |
| .MOV EDX,DWORD PTR SS:[LOCAL.3] | ; set EDX to our current dword | |
| .MOVSX ECX,BYTE PTR DS:[EDX+2] | ; set ECX to dword[2] | |
| .SAR ECX,2 | ; shift right 2 dword[2] | |
| .ADD AL,CL | ; add (shifted left 4 dword[1]) + (shifted right 2 dword[2]) | |
| .MOV EDX,DWORD PTR SS:[LOCAL.5] | ; set EDX to point at our current spot in our decoded buffer | |
| .MOV BYTE PTR DS:[EDX],AL | ; write our decoded value to the decoded buffer | |
| .INC DWORD PTR SS:[LOCAL.5] | ; move to the next spot in our decoded buffer | |
| .MOV EAX,DWORD PTR SS:[LOCAL.3] | ; set EAX to point at our current dword | |
| .MOV CL,BYTE PTR DS:[EAX+2] | ; set ECX/CL to dword[2] | |
| .SHL ECX,6 | ; shift left 6 dword[2] | |
| .MOV EAX,DWORD PTR SS:[LOCAL.3] | ; point EAX at our current dword | |
| .ADD CL,BYTE PTR DS:[EAX+3] | ; add dword[3] + (shifted left 6 dword[2]) | |
| .MOV EDX,DWORD PTR SS:[LOCAL.5] | ; point EDX at our current decoded buffer | |
| .MOV BYTE PTR DS:[EDX],CL | ; write our decoded value to the decoded buffer | |
| .INC DWORD PTR SS:[LOCAL.5] | ; increment our deocded buffer | |
| .MOV ECX,DWORD PTR SS:[ARG.4] | ; set ECX to our current offset? | |
| .ADD DWORD PTR DS:[ECX],3 | ; add 4 for our current byte counter? | |
| .JMP 0A729EA6 | ; jump |
(Dword[0] << 2) + (Dword[1] >> 4) = unencoded byte 1
(Dword[1] << 4) + (Dword[2] >> 2) = unencoded byte 2
(Dword[2] << 6) + Dword[3] = unencoded byte 3


